
How to Maintain and Create OSHA 300 and 300A Safety Forms
In the world of workplace safety and compliance, understanding and properly managing OSHA 300 forms (commonly referred to as OSHA Form 300) and OSHA 300A forms (sometimes called OSHA Form 300A) are essential. These forms are the bedrock of your organization’s safety record-keeping and play a pivotal role in maintaining OSHA compliance. In this blog, we’ll delve into what these forms are, why they matter, and how to ensure you meet OSHA’s stringent requirements.
Explore this Article:
- What Are OSHA 300 and 300A Forms?
- Why Do OSHA 300 and 300A Forms Matter?
- Meeting OSHA Form 300 Requirements
- Filling Out OSHA 300 and 300A Forms Accurately
- Challenges and Tips for Completing OSHA 300 and 300A Forms
- The Road to Safer Workplaces
- Unlocking the Benefits of Accurate OSHA 300 and 300A Record-Keeping
What Are OSHA 300 and 300A Forms?
Let’s start with the basics. OSHA 300 forms are part of a mandatory record-keeping system established by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States. These forms are designed to track and log work-related injuries and illnesses that occur in the workplace.
Now, you might be wondering about OSHA Form 300A. Well, this is a summary of the data collected on Form 300. OSHA Form 300A, also known as the “Summary of Work-Related Injuries and Illnesses,” provides an overview of the total number of incidents, days away from work, and more, making it a valuable tool for both employers and employees.
Why Do OSHA 300 and 300A Forms Matter?
Maintaining accurate and up-to-date OSHA 300 forms is not just a bureaucratic task. It’s a critical aspect of your commitment to workplace safety and OSHA compliance. These forms serve several vital purposes:
- Injury and Illness Tracking: OSHA 300 forms help you keep a detailed record of every work-related injury and illness. This data helps identify patterns and areas in your workplace that may require safety improvements.
- Transparency and Accountability: OSHA Form 300A, when posted in the workplace, informs your employees about the safety situation. It shows that your organization is committed to transparency and accountable for the well-being of its workers.
- Compliance with OSHA Regulations: Failure to maintain accurate OSHA 300 and 300A forms can result in hefty fines and penalties. By staying compliant, you avoid legal troubles and ensure a safer workplace.
- Improvement of Safety Practices: Analyzing the data collected on these forms allows you to pinpoint areas where safety measures can be enhanced, potentially preventing future incidents.

Meeting OSHA Form 300 Requirements
To stay in compliance with OSHA regulations, there are several key steps to follow:
- Proper Record Keeping: Accurate record-keeping is the cornerstone of compliance. Ensure that all injuries and illnesses are documented on OSHA 300 forms promptly and completely.
- Timely Submission: OSHA Form 300A must be filled out annually and posted in the workplace from February 1st to April 30th of each year. Make sure to submit this summary on time.
- Employee Access: Employees have the right to access OSHA Form 300A. Ensure it’s posted in a visible and easily accessible location, such as a break room or common area.
- Review and Analysis: Regularly review the data collected on these forms. Identify trends and patterns, and use this information to improve safety measures.
Filling Out OSHA 300 and 300A Forms Accurately
Now that we’ve covered the importance of OSHA 300 and 300A forms let’s dig into the nitty-gritty of how to correctly complete them. Accuracy is paramount to ensure that your records stand up to OSHA scrutiny and, more importantly, to protect the well-being of your employees.
Step 1: Gather Necessary Information
Before you begin filling out OSHA 300 forms, you need to collect essential information:
- Employee Details: You’ll need the names, job titles, and other relevant details of employees involved in workplace incidents.
- Description of Incident: Document a thorough description of each incident, including the date, time, location, and how it happened.
- Injury or Illness Details: Record the nature of the injury or illness, including affected body parts and any medical treatment provided.
- Days Away from Work: If an employee misses work due to an injury or illness, document the number of days they are away.
Step 2: Classify the Incident
Each incident should be classified into one of several OSHA injury and illness categories. These classifications include:
- Fatal Injury: Any work-related incident that results in an employee’s death.
- Days Away from Work: Cases where employees are unable to work due to injuries or illnesses sustained at work.
- Job Transfer or Restriction: When an employee is transferred to a different job or has work restrictions due to a workplace incident.
- Other Recordable Cases: Injuries or illnesses that don’t fall into the above categories but still require recording.
Step 3: Complete OSHA Form 300
- Use a separate OSHA 300 form for each incident.
- Record incidents in a timely manner. OSHA regulations require that you log incidents within seven calendar days of receiving information that a recordable case has occurred.
- Double-check your entries for accuracy. Errors or incomplete information can lead to compliance issues.
Step 4: Summarize with OSHA Form 300A
At the end of the calendar year, you’ll need to complete OSHA Form 300A, the summary of the year’s incidents. Here’s how:
- Total the number of cases in each category (e.g., total number of days away from work, total job transfers or restrictions).
- Calculate the total number of employee hours worked during the calendar year and the number of employees.
- Calculate the incidence rates.
Step 5: Post OSHA Form 300A
As mentioned earlier, OSHA Form 300A must be posted in the workplace in a conspicuous location where employees can easily access it. Make sure it’s displayed from February 1st to April 30th of the following year.
Step 6: Retain Records
OSHA requires that you retain your OSHA 300 forms, 300A summaries, and the corresponding annual summary for five years. These records may be subject to inspection by OSHA representatives.
Challenges and Tips for Completing OSHA 300 and 300A Forms
As we continue our exploration of OSHA 300 and 300A forms, it’s important to acknowledge that maintaining accurate records can be challenging. However, with the right strategies and attention to detail, you can overcome these challenges and stay in compliance with OSHA regulations.
Challenge 1: Incomplete or Inaccurate Reporting
One common challenge is incomplete or inaccurate reporting of incidents. To address this:
- Train your employees on the importance of timely and accurate reporting.
- Establish a clear reporting process and ensure all employees know how to use it.
- Regularly review reported incidents for accuracy and completeness.
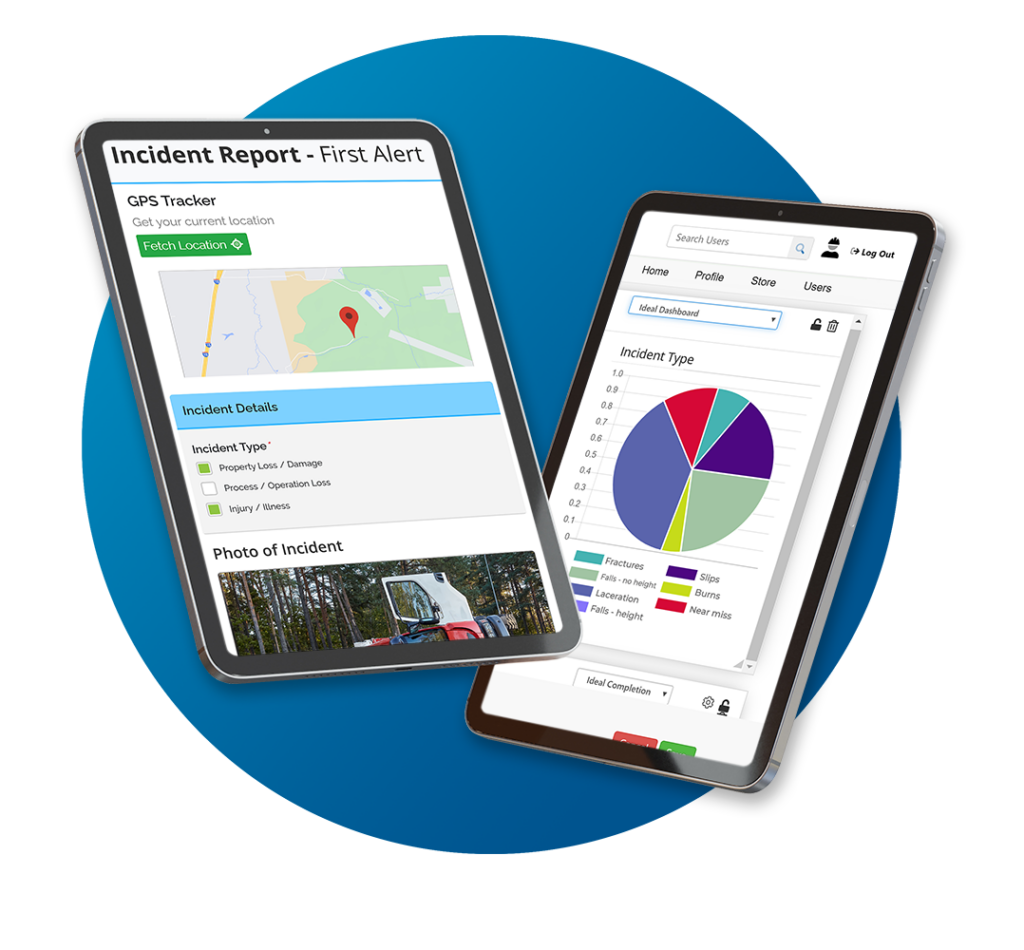
- Implement things to make it easier like Incident Managment Software, or reporting stations.
Challenge 2: Understanding OSHA’s Recordability Criteria
Determining whether an incident should be recorded on OSHA Form 300 can be complex. To navigate this challenge:
- Familiarize yourself with OSHA’s recordability criteria, which are detailed in the OSHA Recordkeeping Handbook.
- Consider seeking guidance from safety professionals or legal experts when in doubt.
Challenge 3: Privacy Concerns
Maintaining employee privacy while recording incidents is crucial. To address this:
- Remove personally identifiable information from incident reports, using only employee IDs or initials.
- Educate employees about privacy measures in place to protect their personal information.
Challenge 4: Calculating Incidence Rates
Calculating incidence rates on OSHA Form 300A can be challenging but is essential for understanding your workplace’s safety trends. Use OSHA’s formulas and guidance for calculating incidence rates, which are as followed:
Recordable Incident Rate (RIR):
- RIR is a measure of the overall safety performance and is calculated using the following formula:
Lost Workday Incident Rate (LWIR):
- LWIR focuses on more severe incidents that result in lost workdays and is calculated using the following formula:
Days Away, Restricted, or Transferred (DART) Rate:
- The DART rate combines cases that result in days away from work, restricted work activity, or job transfer and is calculated as follows:
For a more detailed explanation of how to Calculate Incident Rates see our dedicated article on Total Recordable Incident Rates.
Challenge 5: Compliance with Posting Requirements
Ensuring OSHA Form 300A is posted correctly and on time can be a logistical challenge. To meet these requirements:
- Mark your calendar to remind yourself and your team to post OSHA Form 300A every year from February 1st to April 30th.
- Designate a responsible person or team to oversee this task.
Challenge 6: Record Retention
Keeping records for the required five-year period can be a challenge in terms of storage and organization. To address this:
- Implement a digital record-keeping system to reduce physical storage needs.
- Organize records in a systematic and easily accessible manner.
By addressing these challenges proactively, you can ensure that your OSHA 300 and 300A forms are accurate, compliant, and provide valuable insights into workplace safety.
The Road to Safer Workplaces
Completing and maintaining OSHA 300 and 300A forms might seem like a bureaucratic chore, but it’s a vital step in fostering a safer workplace. These forms serve as a record of your organization’s commitment to the health and well-being of its employees.
Unlocking the Benefits of Accurate OSHA 300 and 300A Record-Keeping
In this final quarter of our series on OSHA 300 and 300A forms, we’ll explore the significant advantages of maintaining accurate records beyond mere compliance. These records, when used effectively, can be powerful tools for improving workplace safety and overall operational efficiency.
1. Identifying Safety Trends
One of the primary benefits of keeping meticulous records is the ability to identify safety trends. By analyzing the data on your OSHA 300 forms over time, you can spot patterns in the types and frequency of workplace incidents. This insight is invaluable for taking proactive measures to address recurring issues and prevent future accidents.
2. Improving Safety Practices
Accurate records provide the foundation for informed decision-making. When you identify trends or areas of concern through your OSHA 300 and 300A forms, you can develop targeted safety initiatives. This might include additional training, better equipment, or enhanced safety protocols, all of which contribute to a safer work environment.
3. Evaluating the Impact of Safety Measures
Recording incidents and analyzing trends allows you to assess the effectiveness of safety measures you’ve implemented. Are your efforts reducing the number of incidents or days away from work? Are job transfers or restrictions decreasing? These forms help you answer these questions and adjust your safety strategies accordingly.
4. Enhancing Employee Awareness
Posting OSHA Form 300A in a visible location in the workplace, as required, sends a powerful message to your employees. It shows that you prioritize their safety and well-being. When workers see this information, it can encourage them to become more safety-conscious, fostering a culture of safety throughout your organization.
5. Building Trust and Accountability
Accurate record-keeping builds trust between employers and employees. When incidents are recorded transparently and privacy is respected, employees are more likely to report incidents promptly. This leads to greater accountability for everyone in the workplace, further contributing to overall safety.
6. Legal Protection
In the unfortunate event of legal disputes or workers’ compensation claims, well-maintained OSHA 300 and 300A forms can serve as valuable evidence. They provide a documented history of incidents and the actions taken by your organization to address them, helping protect your interests in legal matters.
7. Ongoing Compliance
Staying in compliance with OSHA regulations is an ongoing process. Consistent and accurate record-keeping ensures that you’re always prepared for potential OSHA inspections. It also saves you time and stress when it’s time to submit your annual Form 300A summary.
Conclusion: A Safer, More Efficient Workplace
In conclusion, OSHA 300 and 300A forms are not just paperwork. They are essential tools for creating a safer, more efficient workplace. By maintaining accurate records, you can identify trends, improve safety practices, and foster a culture of safety among your employees. These records also provide legal protection and ensure ongoing compliance with OSHA regulations.
Remember, workplace safety is an ongoing commitment. By using OSHA records effectively, you can continuously evolve your safety measures, reduce incidents, and protect your most valuable asset – your employees.
Thank you for joining us on this journey through the world of OSHA 300 and 300A forms. We hope this series has been informative and provided you with the knowledge and motivation to prioritize safety in your workplace.






























